How Starlink Is Different From Fiber & 5G Internet
In today’s connected world, fast and reliable internet is essential, not a luxury. As technology grows, both consumers and businesses have more choices. Each option has its own strengths and weaknesses. It examines its performance, availability, cost, and how well it meets various needs. Knowing these differences is key to choosing the right internet solution for you. This helps close the “digital divide” and improves “network performance”.
In this blog, you’ll explore the key differences between Starlink, Fiber, and 5G to find the best internet fit for your home or business.
1. Starlink: Satellite Internet Reimagined
Starlink is a satellite internet system run by SpaceX. It aims to offer fast, low-latency internet access worldwide. This service is designed for rural areas and places without reliable wired connections. Starlink is different from traditional geostationary satellites. It uses a network of thousands of small “LEO satellites,” which orbit much closer to Earth.
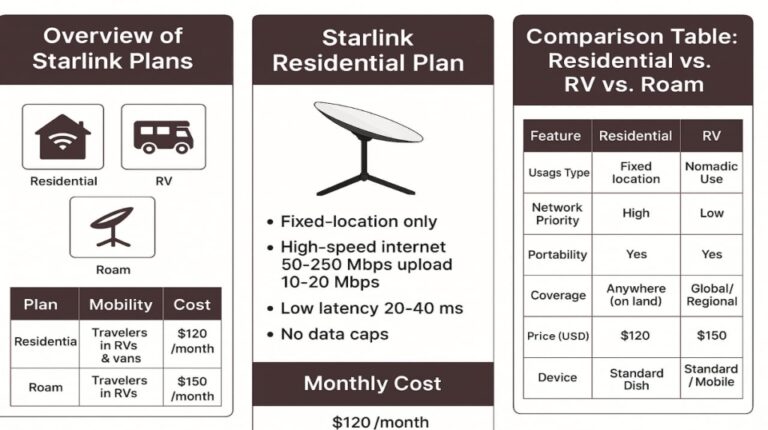
- Speed: Starlink typically offers download speeds ranging from 50 Mbps to 250 Mbps, with upload speeds from 10 Mbps to 20 Mbps. These speeds are much better than older satellite internet. However, they can change due to satellite density, user congestion, and weather conditions.
- Latency: Starlink has a significant edge over traditional satellite internet because of its low latency. It typically ranges from 20 ms to 40 ms. This improvement comes from the closer the LEO satellites are. This makes it better for “real-time applications” like online gaming and video conferencing. These activities were strenuous with earlier satellite connections.
- Availability & Coverage: Starlink offers nearly global coverage, making it an excellent option for remote connectivity. It works well in places where fiber optic internet and cellular networks are lacking. Its primary market is “rural broadband” access. However, it requires a clear view of the sky, and dense obstructions can interfere with the signal received by the “dish.”
- Cost: The initial “cost” for Starlink equipment (the Starlink “dish” and router) can be substantial, often ranging from $499 to $599. Monthly subscription fees are usually higher than regular internet services. They typically range from $90 to $120.
- Reliability: Starlink is mostly reliable. However, severe weather, like heavy rain, snow, or thick clouds, can affect its performance. Network congestion can also occur in areas with many users.
2. Fiber Optic Internet: The Gold Standard
Fiber Optic Internet sends data through light signals, which travel along thin strands of glass or plastic fiber. Fiber optic cables are the fastest and most reliable internet technology available today, providing unmatched performance.
- Speed: Fiber internet provides symmetrical “gigabit speeds.” This means download and upload speeds can hit 1,000 Mbps (1 Gbps) or more. In some places, speeds can reach 2 Gbps, 5 Gbps, 8 Gbps, or even 10 Gbps. High-speed broadband is crucial for heavy internet users, large families, and cloud computing. It supports real-time applications that need a lot of bandwidth.
- Latency: Fiber boasts incredibly “low latency,” typically ranging from 1 ms to 5 ms. This is perfect for sensitive tasks like competitive gaming, live video streaming, and crucial business operations, where instant response times are key.
- Availability & Coverage: “Fiber internet” availability is concentrated in urban and suburban areas, where the “infrastructure” is more economically feasible to deploy. Expanding fiber optic infrastructure to rural areas is a significant investment. This limits its coverage compared to satellite or 5G in less populated regions.
- Cost: Fiber optic internet usually costs between $50 and $100 a month for gigabit plans, which is often competitive with other high-speed options. However, the exact cost can vary by provider and location. Installation fees may apply, but they are sometimes waived. Due to its superior performance, the “cost-effectiveness” over time is often high.
- Reliability: Fiber is very reliable. It’s less affected by electromagnetic signals, weather, or physical wear than copper connections. Most of the “fiber optic infrastructure” is underground, keeping it safe from damage above ground.
3. 5G Wireless Internet: Mobile and Evolving
5G Wireless Internet uses advanced cellular networks to deliver fast internet access. 5G is famous for mobile data on smartphones. Now, it’s also used for fixed wireless home internet.
- Speed: “5G speeds” vary a lot. It depends on the type of 5G you use: low-band, mid-band, or high-band/mmWave. It also relies on how busy the network is and how close you are to a base station.” Download speeds usually range from 50 Mbps to 300 Mbps. In perfect mmWave conditions, peak speeds can exceed 1 Gbps. Upload speeds are typically lower, from 10 Mbps to 50 Mbps.
- Latency: “5G latency” is significantly lower than 4G LTE, often ranging from 10 ms to 30 ms. This makes “5G” suitable for many “real-time applications,” although generally not as low as fiber.
- Availability & Coverage: “5G coverage” is growing fast. Major carriers are investing heavily in “5G cellular networks” for urban, suburban, and some rural areas. It’s built-in “mobile connectivity” is a big plus. It lets users access high-speed internet anywhere. For home internet, it relies on nearby cellular towers.
- Cost: “5G home internet” plans typically cost between $30 and $70 monthly. Sometimes, promotions include equipment.
- Reliability: “5G reliability” relies on signal strength, how far you are from the “base station,” and any obstacles. It is stronger than older wireless tech, but buildings and trees can still block it. Also, network congestion can affect its performance.
Head-to-Head Comparisons
To further clarify the strengths of each technology, let’s look at key comparisons:
- Starlink vs Fiber:
- Speed & Latency: Fiber is generally superior in raw “speed” and “latency” compared to Starlink. Fiber provides symmetrical gigabit speeds with under 10ms latency. In contrast, Starlink has lower speeds and a typical latency of 20-40ms.
- Availability: Starlink works well in remote and rural areas without fiber networks, but fiber is dominant in urban and suburban environments.
- Reliability: Fiber is more reliable than Starlink. It is less affected by the weather and other environmental factors.
- Cost: Starlink usually has a higher upfront equipment cost. Its monthly fees can also be higher than many standard fiber plans, but this can vary.
- Starlink vs 5G:
- Speed: In areas with strong “5G” (especially mmWave), “5G” can offer higher peak speeds than Starlink. Starlink usually offers better broadband access in remote areas, so 5G cellular networks might not work well in these places.
- Latency: “5G latency” is usually lower than Starlink’s. This makes it better for applications that need ultra-low latency.
- Availability: Starlink provides broader geographic “coverage” in extremely remote regions. 5G is growing fast, but it mainly covers busy areas. Fixed wireless access is helping it reach further.
- Mobility: “5G” provides better “mobile connectivity” for moving devices. In contrast, Starlink’s setup is usually fixed.
- Fiber vs 5G:
- Speed & Latency: Fiber leads in speed and latency. It offers fast gigabit connections with minimal delay. While “5G” is quick, its performance can be more variable, and its “latency” is usually higher than fiber’s.
- Reliability: Fiber provides a stable and reliable connection. It is not affected by wireless interference or line-of-sight issues that can impact “5G.”
- Infrastructure: Fiber requires extensive physical “infrastructure” installation, which can be costly and time-consuming. 5G uses current cellular networks to be deployed faster and cheaper in some places.
- Use Cases: Fiber is ideal for demanding fixed applications (e.g., smart homes, extensive online work, large data transfers). 5G is excellent for mobile data and fixed wireless access. It’s perfect where fiber is not available or when mobility matters.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Which internet type is the fastest among Starlink, Fiber, and 5G?
A1: Fiber Optic Internet is generally the most rapid, offering symmetrical gigabit speeds (up to 10 Gbps). 5G has high peak speeds, and Starlink delivers solid satellite speeds. But Fiber gives the most reliable high speeds.
Q2: Which internet connection has the lowest latency?
A2: Fibre optic internet has the lowest latency, usually under 5 milliseconds. This makes it perfect for real-time uses, such as online gaming and video calls. 5G has lower latency than Starlink but still typically higher than fibre.
Q3: Is Starlink a good option for rural areas?
A3: Starlink is an excellent choice for rural and remote areas. Traditional fiber or 5G options may not be available. It provides high-speed, low-latency satellite internet access to underserved regions.
Q4: Can 5G replace fiber internet for home use?
A4: 5G can be a good home internet option (Fixed Wireless Access) where coverage is strong. It provides fast speeds and low latency. Fiber offers more consistent speeds, lower latency, and greater reliability, especially for demanding applications.
Conclusion
Choosing between Starlink, Fiber, and 5G internet relies on your location, broadband needs, and budget.
- Fiber Optic Internet is the top choice for city and suburban dwellers. It offers high speed, low latency, and excellent reliability.” It’s perfect for online gaming, streaming 4K or 8K, and moving large files. It works well in homes with many connected devices.
- Starlink helps users in remote or rural areas. It offers “high-speed broadband” where traditional options are limited or missing. It has higher initial costs and a bit more “latency” than fiber, but it can provide unmatched “internet connectivity” to those who don’t have it.
- 5G Wireless Internet offers great speed and flexibility. It’s an excellent option for those with poor 5G coverage, especially if fiber is unavailable. It competes well with cable internet and is excellent for mobile connectivity. As emerging network technologies advance, 5 G’s performance and coverage will improve.